Understanding pain medications is essential for every nurse, particularly those preparing for the NCLEX or using a nursing bundle to master pharmacology. Whether you are a registered nurse (RN nurse) working at the bedside or a student advancing in your nursing education, knowing how to choose, administer, and monitor pain medications is critical for patient care.
This guide simplifies the differences between opioids, NSAIDs, and acetaminophen, helping you provide safe, effective relief while minimizing risks.
💡 Why Pain Management Matters in Nursing
Pain ranks among the most common symptoms patients experience. Consequently, managing it effectively requires knowledge of how medications work. Proper pain management improves outcomes, increases comfort, and supports faster recovery. Moreover, NCLEX success depends on understanding how different drugs are selected based on the patient’s condition, pain level, and risk factors.
🔍 Overview: 3 Main Categories of Pain Medications
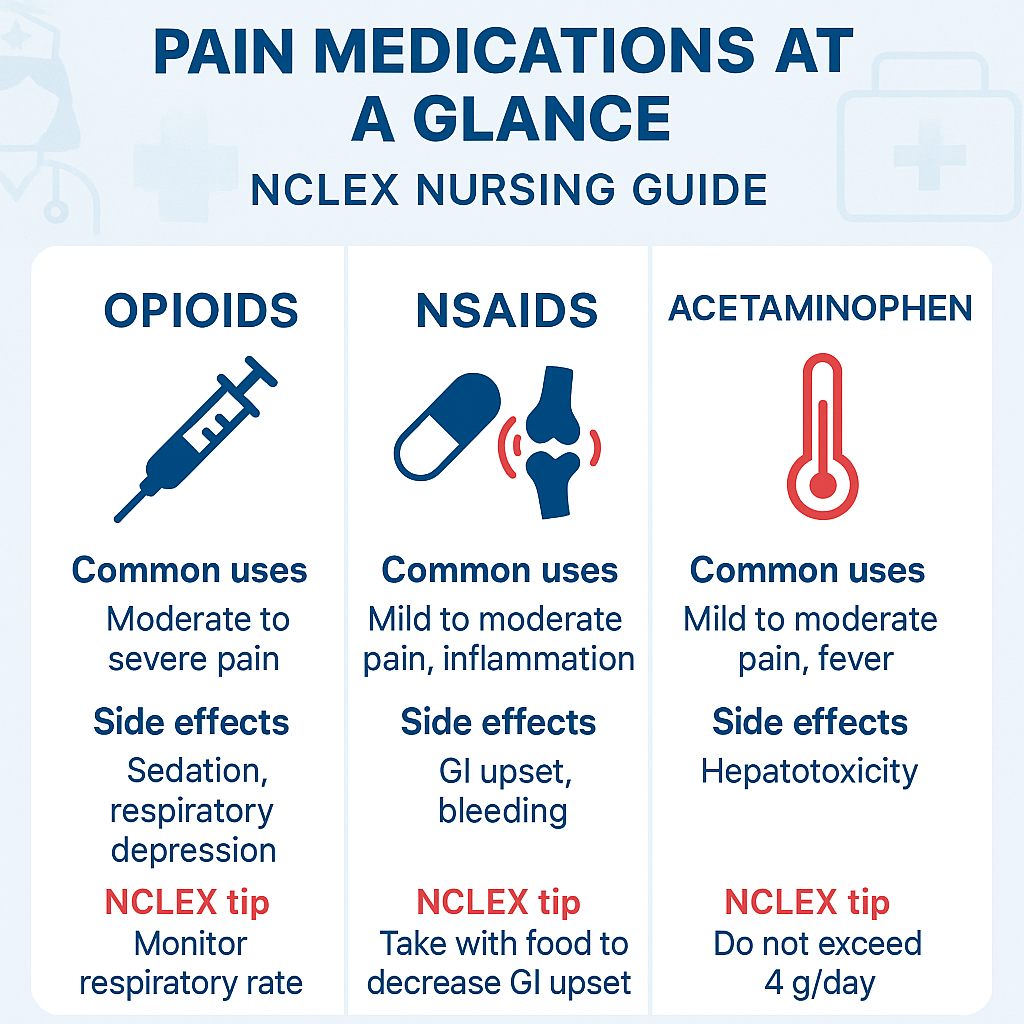
| Medication Type | Examples | Common Use | NCLEX Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Opioids | Morphine, Oxycodone | Severe pain | Respiratory depression |
| NSAIDs | Ibuprofen, Naproxen | Mild to moderate pain, inflammation | GI bleeding, kidney risk |
| Acetaminophen | Tylenol | Mild to moderate pain, fever | Liver toxicity, max dose alerts |
🧠 Opioids: Powerful but High Risk
How They Work:
Opioids bind to receptors in the brain and spinal cord to block pain. Nurses commonly use them for acute severe pain, such as post-surgical pain or trauma.
Common Side Effects:
- Drowsiness
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Respiratory depression (💥 NCLEX alert!)
RN Nurse Tips:
- Always monitor respiratory rate closely and hold the dose if it drops below 12 breaths/min.
- Use opioids cautiously in elderly or opioid-naïve patients.
- Encourage fluids and fiber to prevent constipation.
- Apply pain scales (0–10) to guide administration.
NCLEX Keywords:
- “Morphine – hold if respirations are low”
- “Naloxone (Narcan) is the antidote for opioid overdose”
🔬 NSAIDs: The Anti-Inflammatory Heroes
How They Work:
NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) reduce inflammation. They work well for musculoskeletal pain, arthritis, menstrual cramps, and fever.
Common Side Effects:
- GI upset
- Gastric ulcers
- Kidney impairment (especially with long-term use)
- Increased bleeding risk
RN Nurse Tips:
- Administer with food to reduce stomach irritation.
- Avoid in patients with kidney issues or peptic ulcers.
- Monitor creatinine and BUN for long-term therapy.
- Watch for bleeding signs like bruising or black stool.
NCLEX Keywords:
- “NSAIDs + anticoagulants = bleeding risk”
- “Avoid NSAIDs in renal impairment”
🌡 Acetaminophen: Go-To for Fever & Mild Pain
How It Works:
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) reduces pain and fever, although it does not act as an anti-inflammatory. Nurses often use it when NSAIDs are contraindicated.
Common Side Effects:
- Liver damage (especially with overdose or chronic use)
RN Nurse Tips:
- Keep the maximum dose at 4,000 mg/day for adults.
- Assess liver function tests (AST, ALT) regularly.
- Educate patients about hidden acetaminophen in combination drugs (e.g., cold medications).
NCLEX Keywords:
- “Monitor liver function with acetaminophen”
- “Acetaminophen toxicity = antidote is acetylcysteine”
🧾 When to Use Each: Quick Nursing Bundle Table
| Situation | Preferred Drug | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Post-op severe pain | Opioids | Strongest relief |
| Fever with liver disease | NSAIDs (cautiously) | Avoid Tylenol due to liver risk |
| Headache or minor pain | Acetaminophen | Safer, fewer side effects |
| Arthritis or inflammation | NSAIDs | Reduces swelling and pain |
| Chronic pain (risk of addiction) | Acetaminophen or NSAIDs | Avoid opioids, use cautiously |
⚠️ Safety Tips for RN Nurses
To protect patients, always:
- Double-check allergies before administering medications.
- Follow the 5 rights of medication administration.
- Assess pain before and after giving meds to evaluate effectiveness.
- Document side effects and notify the provider when necessary.
📚 NCLEX Focus: What You Must Know
For NCLEX preparation, nurses must monitor both the effectiveness of medications and early signs of complications. Pain medications are high-yield topics. Understanding the differences between opioids, NSAIDs, and acetaminophen helps ensure safe practice and confident exam performance.
✅ Final Takeaways
- Opioids are effective but risky—monitor breathing and LOC closely.
- NSAIDs reduce inflammation but may harm the GI tract and kidneys.
- Acetaminophen is safe when dosed correctly, yet liver damage remains a concern.
- As an RN nurse, you serve as the first line of defense against side effects and medication errors.
Adding this guide to your nursing bundle provides a handy reference sheet. Share it with fellow nursing students preparing for the NCLEX to boost their confidence and knowledge.