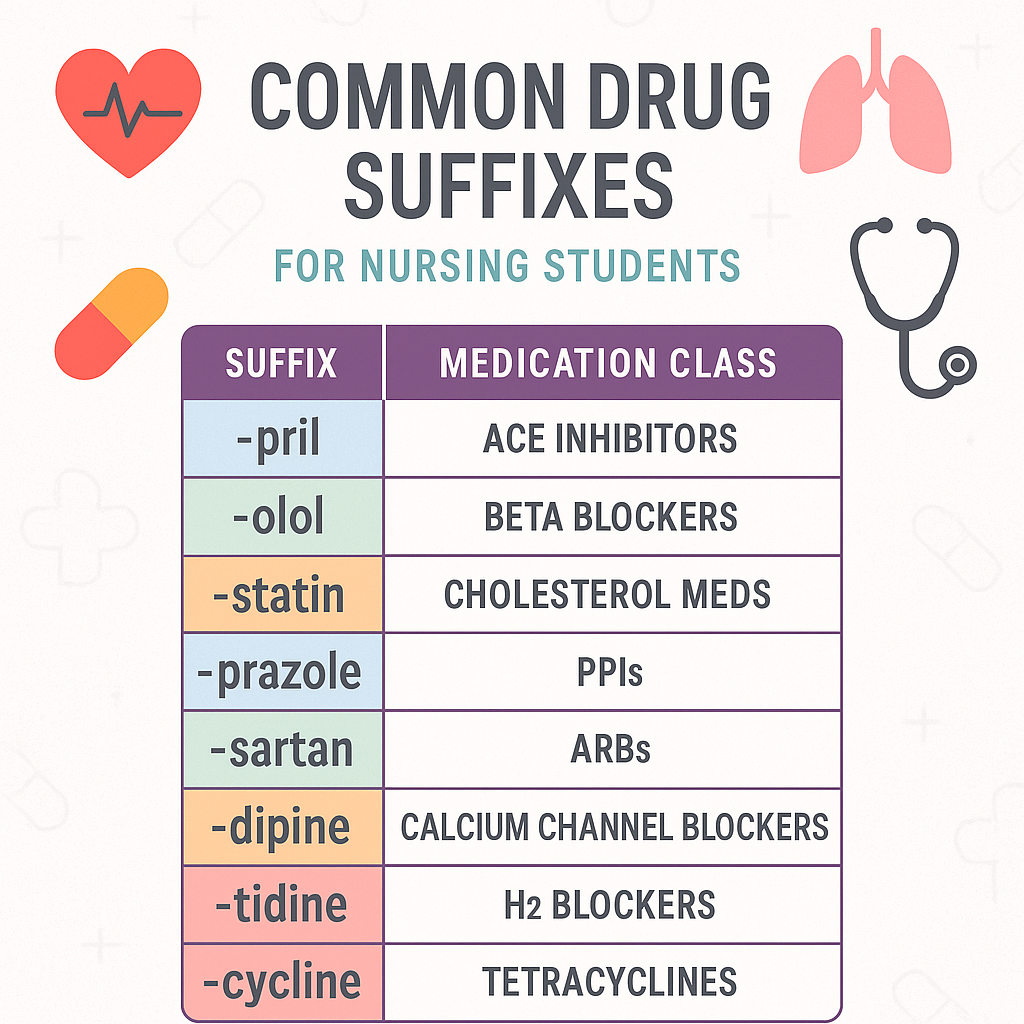
One of the best hacks for memorizing medications for the NCLEX is to learn drug suffixes. Whether you’re a nursing student, a registered nurse (RN nurse), or building your nursing bundle of study guides, recognizing drug endings helps you identify the drug class and anticipate side effects, uses, and red flags.
This cheat sheet simplifies complex pharmacology and is perfect for quick reference and review.
🧠 Why Drug Suffixes Matter for Nurses and the NCLEX
On the NCLEX, you won’t always get the full breakdown of a medication—just the name. Knowing common suffixes can help you:
- Recognize the drug class instantly
- Predict side effects and contraindications
- Answer NCLEX questions quickly and confidently
- Improve patient safety as a nurse
💊 Common Drug Suffixes Every RN Nurse Should Know
Here’s a breakdown of the most high-yield suffixes used in nursing and NCLEX prep:
1. -pril → ACE Inhibitors
Example: Lisinopril, Enalapril
- Use: Hypertension, heart failure
- Key Side Effect: Dry cough, angioedema, hyperkalemia
- NCLEX Tip: Avoid in pregnancy
2. -sartan → ARBs (Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers)
Example: Losartan, Valsartan
- Use: Hypertension
- Key Side Effect: Hyperkalemia, no cough
- RN Nurse Reminder: Good alternative for patients who can’t tolerate ACE inhibitors
3. -olol → Beta Blockers
Example: Metoprolol, Propranolol
- Use: Hypertension, arrhythmias, heart failure
- Side Effects: Bradycardia, fatigue, hypotension
- Nursing Alert: Hold if HR < 60 bpm
4. -dipine → Calcium Channel Blockers
Example: Amlodipine, Nifedipine
- Use: Hypertension, angina
- Watch for: Peripheral edema, hypotension
- NCLEX Hint: Monitor BP and HR
5. -statin → Cholesterol-lowering drugs
Example: Atorvastatin, Simvastatin
- Use: High cholesterol, cardiovascular prevention
- Side Effects: Muscle pain (rhabdomyolysis), liver damage
- RN Tip: Take in the evening; avoid grapefruit juice
6. -prazole → Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
Example: Omeprazole, Pantoprazole
- Use: GERD, ulcers
- Side Effects: Risk of osteoporosis, C. diff
- RN Nurse Tip: Long-term use increases fracture risk
7. -tidine → H2 Blockers
Example: Ranitidine, Famotidine
- Use: GERD, acid reduction
- Key Side Effect: Rare, but can cause confusion in elderly
- Nursing Pearl: Take before meals
8. -cillin / -cycline / -mycin / -floxacin → Antibiotics
- Examples:
- Penicillin → Amoxicillin
- Tetracycline → Doxycycline
- Macrolide → Azithromycin
- Fluoroquinolone → Ciprofloxacin
- RN Tips: Watch for allergies, GI upset, and photosensitivity
9. -mab / -nib → Monoclonal Antibodies & Kinase Inhibitors (Immunotherapy/Oncology)
Example: Adalimumab, Imatinib
- Use: Autoimmune disorders, cancer
- Watch for: Immunosuppression, infection risk
- NCLEX Note: Report fever or signs of infection immediately
10. -ide → Loop Diuretics/Sulfonylureas
Example: Furosemide (loop), Glipizide (sulfonylurea)
- Loop Diuretics Side Effect: Hypokalemia, dehydration
- Sulfonylurea Side Effect: Hypoglycemia
- RN Nurse Action: Monitor labs and blood sugar
11. -lam / -pam → Benzodiazepines
Example: Diazepam, Lorazepam
- Use: Anxiety, seizures, sedation
- Warning: Respiratory depression, dependence
- NCLEX Tip: Fall risk for elderly patients
12. -caine → Local Anesthetics
Example: Lidocaine
- Use: Numbing agent for minor procedures
- Adverse Effect: CNS depression if systemic
13. -asone / -solone → Corticosteroids
Example: Prednisone, Dexamethasone
- Use: Inflammation, autoimmune diseases
- Side Effects: Hyperglycemia, osteoporosis, infection
- RN Nurse Advice: Don’t stop abruptly
14. -zine / -dronate / -lone → Various Specialty Drugs
- Hydroxyzine: Antihistamine
- Alendronate: Bone density (osteoporosis)
- Methylprednisolone: Steroid anti-inflammatory
📋 Quick Reference Table: Drug Suffix Guide
| Suffix | Drug Class | Example | Nursing Alert |
|---|---|---|---|
| -pril | ACE Inhibitor | Lisinopril | Watch for cough |
| -sartan | ARB | Losartan | Monitor K+ |
| -olol | Beta Blocker | Metoprolol | Hold if HR < 60 |
| -dipine | CCB | Amlodipine | Watch for edema |
| -statin | Cholesterol | Atorvastatin | Check liver enzymes |
| -prazole | PPI | Omeprazole | Bone loss with long-term use |
| -tidine | H2 Blocker | Ranitidine | Take before meals |
| -cillin | Penicillin | Amoxicillin | Allergy risk |
| -floxacin | Fluoroquinolone | Ciprofloxacin | Avoid sun exposure |
| -mab | Monoclonal Ab | Adalimumab | Infection risk |
| -pam | Benzodiazepine | Lorazepam | Sedation warning |
📝 Final NCLEX and Nursing Review Tips
Mastering drug suffixes is a smart NCLEX strategy. It saves time and helps you act fast in real clinical settings. Add this guide to your nursing bundle so you can review often!
Whether you’re a student nurse, RN nurse, or registered nurse building your med-surg skills, suffix knowledge keeps your practice sharp and your patients safe.