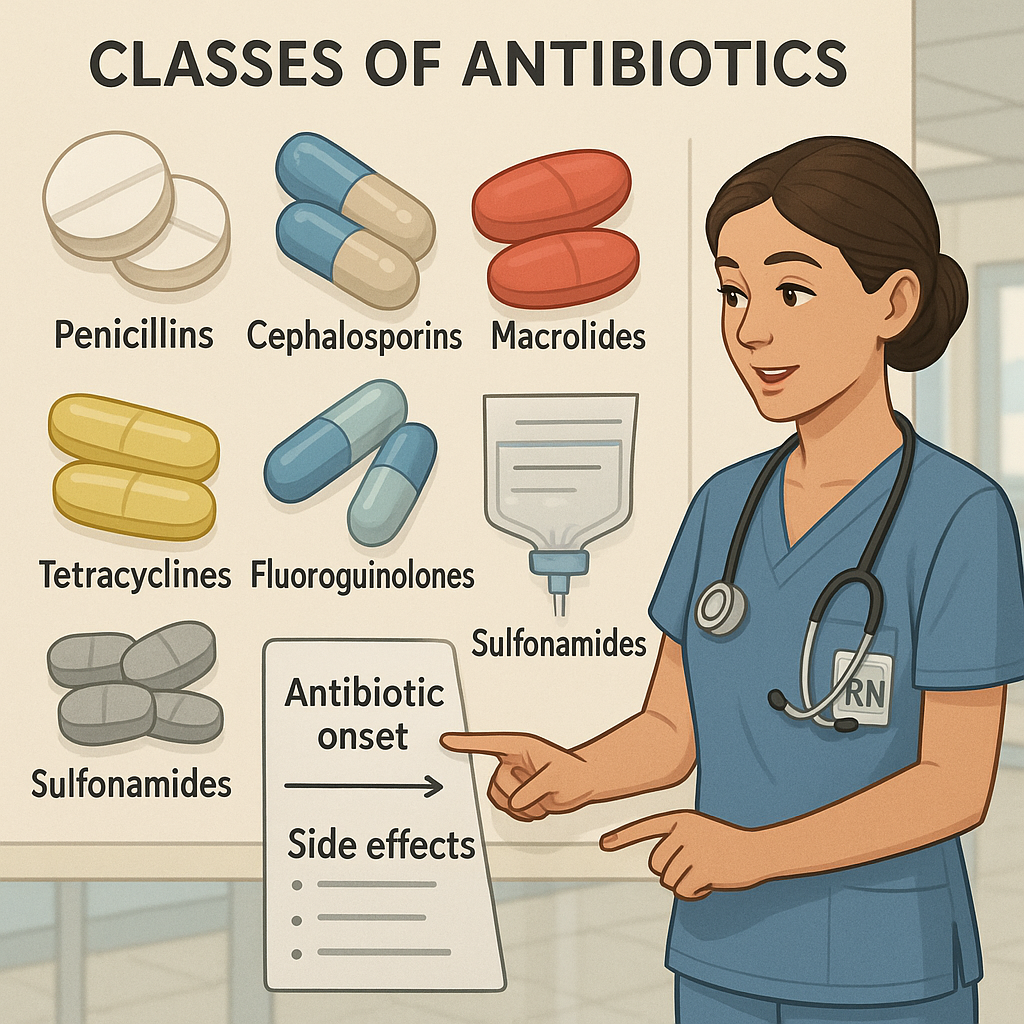
Antibiotics are one of the most tested topics on the NCLEX and a critical area for every nurse to master. Whether you’re a registered nurse (RN nurse) on the floor or a student preparing with a nursing bundle, understanding antibiotic classes, nursing considerations, and common side effects is essential for safe patient care.
📌 Major Classes of Antibiotics
1. Penicillins
- Examples: Amoxicillin, Penicillin G
- Uses: Strep throat, syphilis, skin infections
- Nursing Tips: Watch for allergic reactions (especially in patients with cephalosporin allergies).
- Side Effects: Rash, diarrhea, anaphylaxis
2. Cephalosporins
- Examples: Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone
- Uses: Respiratory infections, UTIs, skin infections
- Nursing Tips: Assess for penicillin allergy cross-sensitivity. Avoid alcohol (risk of disulfiram-like reaction).
- Side Effects: GI upset, superinfections, hypersensitivity
3. Macrolides
- Examples: Azithromycin, Erythromycin
- Uses: Respiratory infections, chlamydia, pertussis
- Nursing Tips: Take on an empty stomach. Monitor for prolonged QT interval.
- Side Effects: GI upset, liver toxicity, arrhythmias
4. Fluoroquinolones
- Examples: Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin
- Uses: UTIs, pneumonia, bone/joint infections
- Nursing Tips: Avoid in children (risk of tendon rupture). Take 2 hrs before or after antacids.
- Side Effects: Photosensitivity, tendon rupture, dizziness
5. Tetracyclines
- Examples: Doxycycline, Tetracycline
- Uses: Acne, Lyme disease, chlamydia
- Nursing Tips: Do not give to children <8 or pregnant women (tooth discoloration, bone growth inhibition). Avoid dairy and antacids.
- Side Effects: Photosensitivity, GI upset, hepatotoxicity
6. Aminoglycosides
- Examples: Gentamicin, Tobramycin
- Uses: Severe Gram-negative infections, sepsis
- Nursing Tips: Monitor peak and trough levels to avoid toxicity.
- Side Effects: Nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity
7. Sulfonamides
- Examples: Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim)
- Uses: UTIs, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia
- Nursing Tips: Encourage hydration to prevent kidney stones. Watch for sulfa allergy.
- Side Effects: Photosensitivity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, bone marrow suppression
🩺 Nursing Considerations for Antibiotics
- Always check allergies before giving an antibiotic.
- Educate patients to complete the full course (to prevent resistance).
- Monitor for signs of superinfection (C. diff, oral thrush).
- Teach patients about sun precautions with tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones.
- Assess renal and hepatic function before prolonged therapy.
💡 NCLEX Quick Tips
- If a patient reports difficulty breathing after penicillin, stop the medication and prepare for emergency interventions.
- Gentamicin toxicity = think ears and kidneys.
- Doxycycline + pregnancy = contraindicated.
These are classic NCLEX-style points that every nurse should review while studying from a nursing bundle or preparing for clinical practice as a registered nurse (RN nurse).