Understanding insulin types is essential for every nurse, especially when preparing for the NCLEX or caring for patients with diabetes. Whether you’re a registered nurse (RN nurse), nursing student, or building your nursing bundle of study resources, mastering insulin action times helps you provide safe, effective care.
This article simplifies insulin into an easy-to-understand format—complete with a chart showing onset, peak, and duration—perfect for NCLEX prep and bedside practice.
🧠 Why Insulin Knowledge Matters for NCLEX and Nursing
Insulin is a high-alert medication. The wrong timing or type can lead to hypoglycemia or poor blood glucose control. For RN nurses and students alike, knowing insulin types is a must-have skill for clinical practice and exam success.
NCLEX Tip: Expect insulin questions in pharmacology and diabetes management sections. You’ll need to match the right type to a scenario.
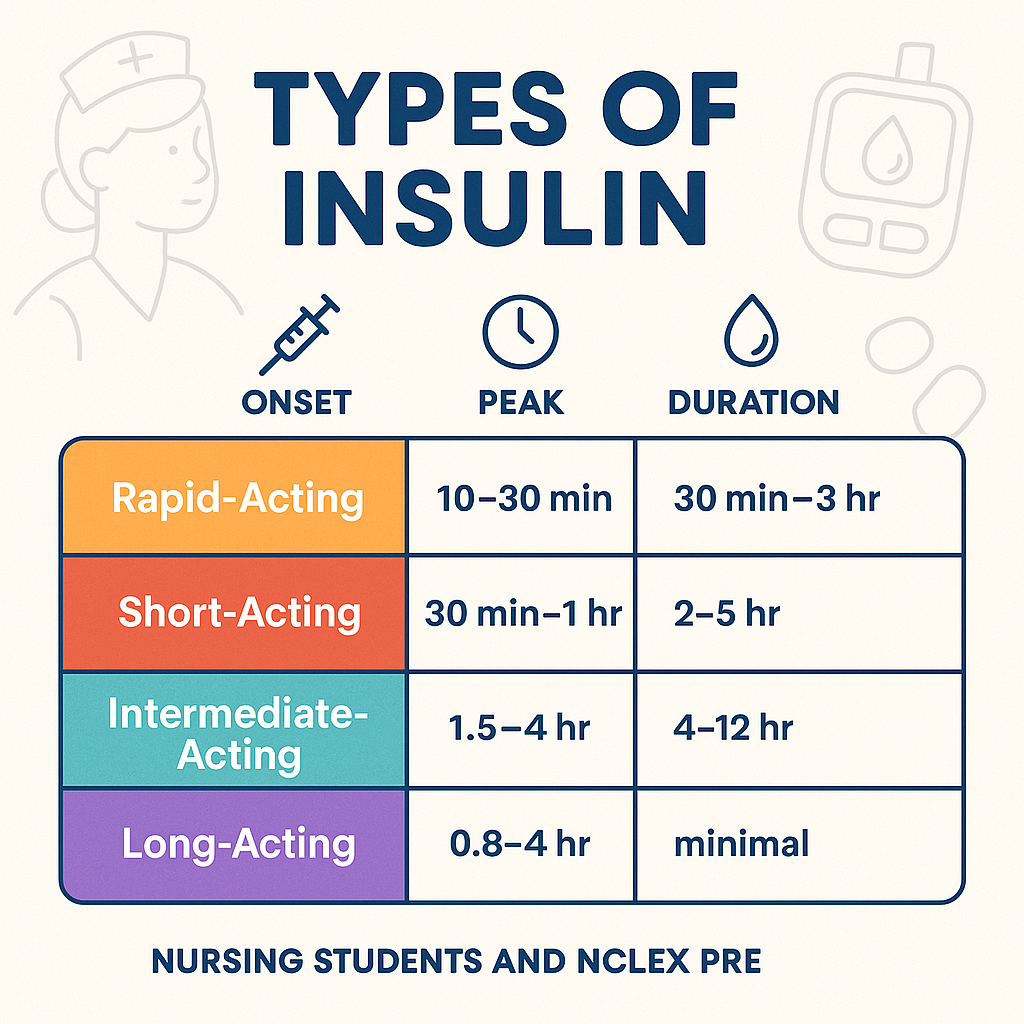
💉 4 Main Types of Insulin
Insulin is classified based on how quickly it works and how long it stays active in the body. Here’s a breakdown of the main types every nurse should know:
1. Rapid-Acting Insulin
- Examples: Lispro (Humalog), Aspart (Novolog), Glulisine (Apidra)
- Onset: 10–30 minutes
- Peak: 30 minutes – 3 hours
- Duration: 3–5 hours
- Nursing Tip: Give right before meals; watch for hypoglycemia soon after eating.
2. Short-Acting Insulin (Regular)
- Examples: Regular (Humulin R, Novolin R)
- Onset: 30–60 minutes
- Peak: 2–5 hours
- Duration: 5–8 hours
- Nursing Tip: Can be given IV; used in DKA treatment.
3. Intermediate-Acting Insulin
- Examples: NPH (Humulin N, Novolin N)
- Onset: 1.5–4 hours
- Peak: 4–12 hours
- Duration: 12–18 hours
- Nursing Tip: Often given twice daily; may be cloudy (roll before use).
4. Long-Acting Insulin
- Examples: Glargine (Lantus), Detemir (Levemir), Degludec (Tresiba)
- Onset: 1–4 hours
- Peak: Minimal to none
- Duration: Up to 24+ hours
- RN Reminder: Do not mix with other insulins in same syringe.
📊 Insulin Onset, Peak, Duration Chart for Nurses
| Insulin Type | Onset | Peak | Duration | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid-Acting | 10–30 min | 30 min – 3 hrs | 3–5 hrs | Lispro, Aspart, Glulisine |
| Short-Acting (Regular) | 30–60 min | 2–5 hrs | 5–8 hrs | Regular (Humulin R) |
| Intermediate-Acting | 1.5–4 hrs | 4–12 hrs | 12–18 hrs | NPH |
| Long-Acting | 1–4 hrs | None/Minimal | 24+ hrs | Glargine, Detemir, Degludec |
🧪 Mixing Insulin: What Every RN Nurse Should Know
Some insulin types can be mixed, but there are rules:
- Clear before cloudy (draw up regular insulin before NPH)
- Do not mix long-acting insulin (like Glargine or Detemir) with any other insulin
- Use within 5–15 minutes of mixing
⏰ NCLEX-Style Nursing Interventions
- Monitor for hypoglycemia: Especially at insulin peak times
- Rotate injection sites: Prevent lipodystrophy
- Educate patients: On timing meals and recognizing hypoglycemia symptoms
- Check blood glucose: Before administering insulin
- Know your institution’s protocol: For insulin sliding scale or correctional insulin
💡 Pro Nurse Tips for Insulin Safety
- Keep insulin refrigerated if unopened.
- Once opened, store at room temperature (check expiration guidelines).
- Always use insulin syringes for accuracy.
- Double-check insulin doses—especially high-risk in pediatrics or critical care.
- Always label mixed doses if not used immediately.
🎓 NCLEX Example Question
Question: A nurse prepares to administer Lispro insulin. The client’s breakfast tray has not arrived yet. What should the nurse do?
A. Administer the insulin and monitor for hypoglycemia
B. Hold the insulin until the tray arrives ✅
C. Administer regular insulin instead
D. Call the provider to change the insulin type
Rationale: Rapid-acting insulin should be given with or just before meals to prevent hypoglycemia.
📝 Final Review: Why This Belongs in Your Nursing Bundle
Every nursing bundle for med-surg, endocrine, or pharmacology should include this insulin guide. It makes your NCLEX review easier, improves patient safety, and gives you the confidence to manage diabetic care.
Whether you’re a student nurse, a newly licensed RN nurse, or preparing a registered nurse practice exam, insulin action times are something you’ll use every shift.