Stroke is a leading cause of disability and death worldwide, and every nurse, especially a registered nurse (RN nurse), must be ready to respond. Understanding the difference between ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, and knowing how to prioritize care, is essential for safe practice and for success on the NCLEX.
This simplified nursing guide will help you build your nursing bundle and feel confident caring for stroke patients.
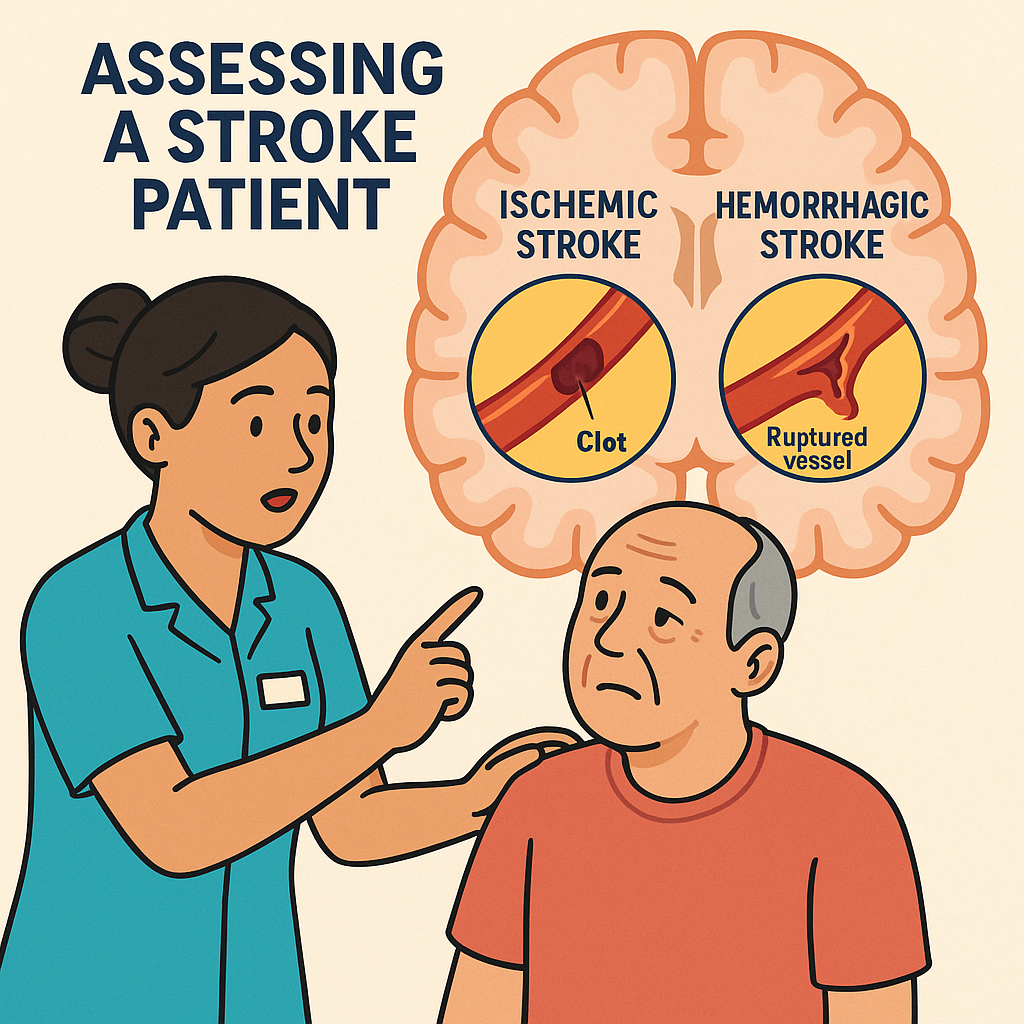
🧠 What is a Stroke?
A stroke happens when blood flow to part of the brain is blocked or when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. Without oxygen, brain cells begin to die within minutes.
There are two major types of strokes:
✅ Ischemic Stroke — caused by a clot blocking blood flow
✅ Hemorrhagic Stroke — caused by bleeding in the brain
Ischemic Stroke: Nursing Priorities
Ischemic strokes account for about 85% of strokes. They are caused by a thrombus (stationary clot) or embolus (traveling clot) blocking an artery supplying the brain.
Key NCLEX Nursing Points for Ischemic Stroke:
- Time is brain — get a last known well time for possible tPA treatment
- Support airway, breathing, and circulation
- Maintain oxygen saturation above 94%
- Keep blood pressure within recommended guidelines
- Prepare for possible thrombolytic therapy (alteplase/tPA)
- Frequent neuro checks (use NIH Stroke Scale)
- Monitor for bleeding after tPA administration
- Prevent aspiration — keep patient NPO until swallow evaluation
Signs & Symptoms (FAST):
✅ Face drooping
✅ Arm weakness
✅ Speech difficulty
✅ Time to call 911
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Nursing Priorities
Hemorrhagic strokes happen when a blood vessel ruptures, causing bleeding in or around the brain.
Common causes include:
✅ Uncontrolled hypertension
✅ Aneurysm rupture
✅ AV malformation rupture
Key NCLEX Nursing Points for Hemorrhagic Stroke:
- Strict BP control to prevent further bleeding
- Avoid anticoagulants
- Prepare for neurosurgical intervention if ordered
- Keep patient on bedrest with head of bed elevated 30 degrees
- Monitor for increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
- Frequent neuro checks and seizure precautions
- Limit stimulation to reduce blood pressure spikes
Signs & Symptoms:
✅ Sudden severe headache (“worst headache of my life”)
✅ Nausea/vomiting
✅ Loss of consciousness
✅ Seizures
Registered Nurse Priorities for All Strokes
Every RN nurse should remember these stroke essentials:
✅ ABCs first — airway, breathing, circulation
✅ Get a CT scan STAT to differentiate ischemic vs. hemorrhagic
✅ Perform frequent neuro assessments
✅ Keep the patient safe from injury
✅ Educate the family on stroke warning signs
✅ Coordinate rehab and therapy referrals
NCLEX & Nursing Bundle Cheat Sheet
Add these to your nursing bundle:
- FAST stroke recognition poster
- NIH Stroke Scale quick guide
- tPA contraindications chart
- Hemorrhagic vs. ischemic differences cheat sheet
- Stroke diet and aspiration risk guide
These will help you pass the NCLEX and deliver safe, evidence-based care.
🧩 Quick Memory Tips
💡 Ischemic = clot
💡 Hemorrhagic = bleed
💡 “Time is brain” — minutes matter
💡 Worst headache of my life = think bleed
📚 Patient and Family Education
✅ Importance of taking antihypertensive medications
✅ Recognize FAST warning signs early
✅ Stop smoking and manage cholesterol
✅ Follow a heart-healthy diet
✅ Participate in rehab therapy for maximum recovery