Schizophrenia is a complex mental health disorder that every nurse should understand. It often appears on the NCLEX exam and is a key topic in many nursing bundles. By knowing the difference between positive and negative symptoms, any registered nurse (RN nurse) can provide better care and keep patients safe.
🧠 What Is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a chronic brain disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It can cause hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech, and trouble with daily activities. Patients may have difficulty knowing what is real and what is not.
📌 Positive vs. Negative Symptoms
In nursing, schizophrenia symptoms are divided into positive and negative categories. This helps the RN nurse understand how the disease changes a patient’s behavior.
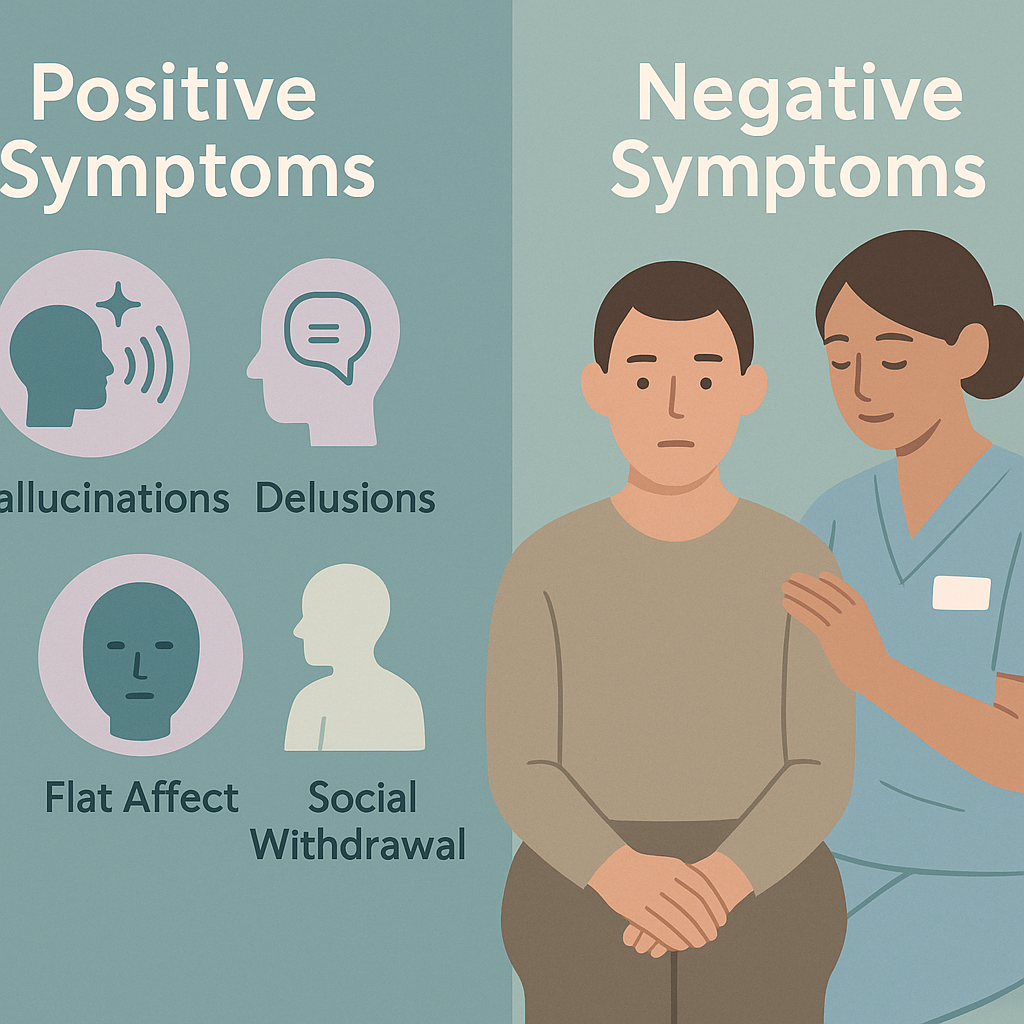
➕ Positive Symptoms
Positive doesn’t mean “good.” It means added behaviors that are not normally present.
Examples:
- Hallucinations: Seeing or hearing things that aren’t there. Hearing voices is most common.
- Delusions: False beliefs. For example, thinking they are famous or that someone is spying on them.
- Disorganized speech: Talking in ways that are hard to follow.
- Bizarre behavior: Unpredictable or inappropriate actions.
Nursing tip: Patients with positive symptoms may be very frightened or agitated. Stay calm, speak clearly, and don’t argue with their beliefs.
➖ Negative Symptoms
Negative means “something is missing.” These are behaviors or emotions that are reduced or absent.
Examples:
- Flat affect: No emotional expression.
- Alogia: Little speech.
- Anhedonia: No pleasure in activities.
- Avolition: Lack of motivation to do daily tasks.
- Social withdrawal: Avoiding people or activities.
Nursing tip: Negative symptoms often make self-care and social interaction hard. Encourage small goals and give praise for effort.
🩺 Nursing Care for Schizophrenia
Here’s what every RN nurse should know:
✅ Build trust: Be consistent and honest. Patients may not trust easily.
✅ Monitor safety: Hallucinations or delusions can lead to risky behavior. Protect patients and others.
✅ Use clear communication: Short, simple sentences help avoid confusion.
✅ Do not argue: Do not challenge hallucinations or delusions. Instead, respond calmly and redirect if needed.
✅ Encourage self-care: Assist with hygiene and eating if negative symptoms are severe.
📚 Schizophrenia and the NCLEX
👉 For NCLEX questions:
- Positive = hallucinations, delusions.
- Negative = flat affect, withdrawal.
- Focus on safety first and therapeutic communication.
Use your nursing bundle or class notes to review antipsychotic medications and side effects like tardive dyskinesia or neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
✅ Key Takeaway
Registered nurses must understand both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia to give compassionate, safe care. By recognizing signs early, you can help patients manage their condition and improve their quality of life.