Placental complications are among the most critical emergencies every nurse, registered nurse, and RN nurse must understand. Both placenta previa and placental abruption can threaten the lives of both mother and fetus. These topics frequently appear on the NCLEX, making them essential additions to any nursing bundle.
🩺 What is Placenta Previa?
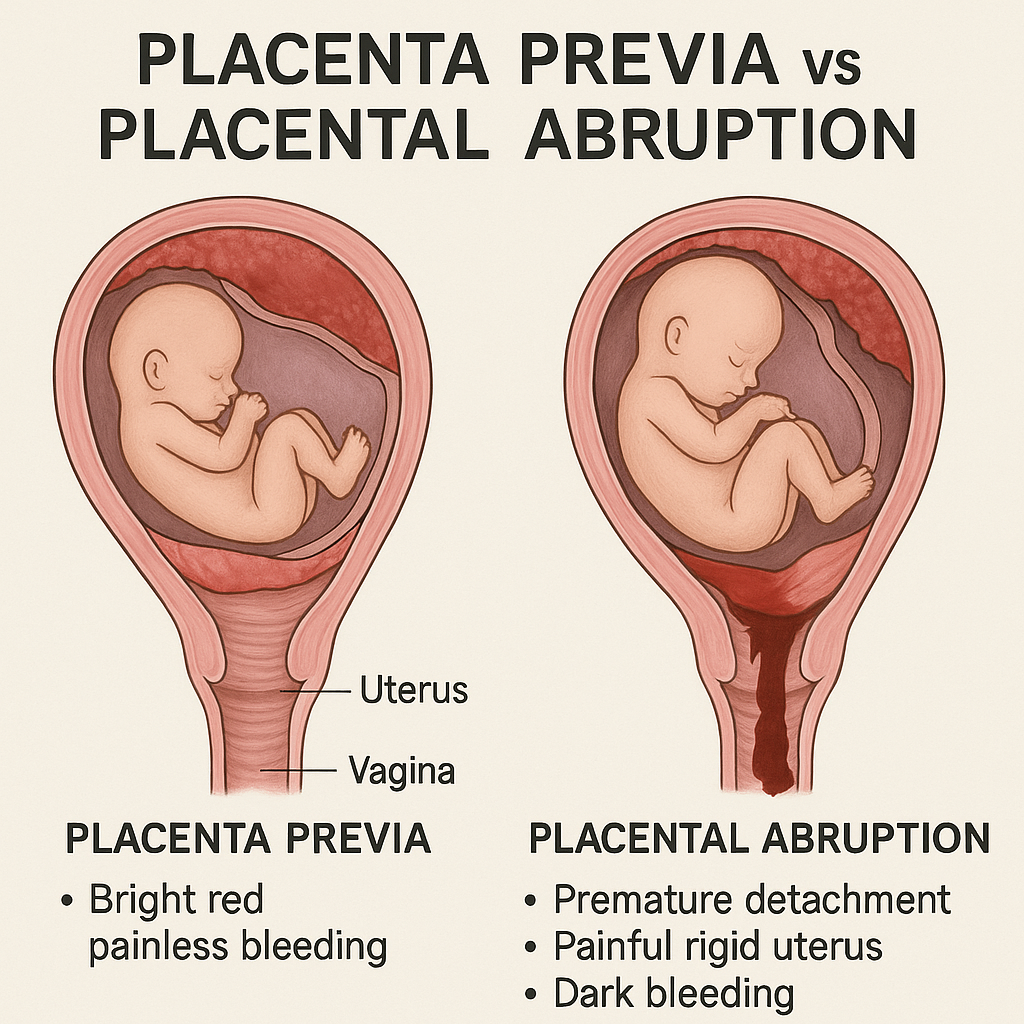
Placenta previa happens when the placenta implants low in the uterus, partially or completely covering the cervical opening (the internal os). This condition can cause painless, bright-red vaginal bleeding in the second or third trimester.
Key Points for Nursing:
✅ Placenta covers the cervix
✅ Bleeding usually painless
✅ Risks increase with prior cesarean section, advanced maternal age, or multiple gestations
✅ Diagnosed by ultrasound — no vaginal exams
⚠️ Placental Abruption Explained
Placental abruption occurs when the placenta detaches prematurely from the uterine wall. This condition is painful, and the bleeding may be visible (external) or hidden (concealed).
Key Points for Nursing:
✅ Placenta separates early
✅ Painful, rigid abdomen
✅ Dark red bleeding
✅ High risk for fetal distress or maternal hypovolemic shock
✅ Often associated with hypertension, trauma, smoking, or cocaine use
🟡 Nursing Priorities for Placenta Previa
Every registered nurse and RN nurse must memorize these priorities:
- Avoid vaginal exams (risk of provoking massive bleeding)
- Monitor maternal vital signs and fetal heart rate
- Assess bleeding amount and color
- Prepare for cesarean delivery if significant bleeding occurs
- Educate patient on pelvic rest (no intercourse, no vaginal exams)
These steps help keep both mother and fetus safe — a must-know for your NCLEX study plan or nursing bundle.
🟢 Nursing Priorities for Placental Abruption
Placental abruption is a true obstetric emergency. Nursing priorities include:
- Call for immediate help — high-risk for fetal death
- Administer oxygen to support fetal oxygenation
- Start large-bore IV lines for fluid and possible blood transfusion
- Monitor fetal heart tones continuously
- Prepare for emergency cesarean section if fetal distress is present
- Provide emotional support to the mother and family
NCLEX tip: Placental abruption = painful bleeding with a rigid, boardlike abdomen.
🩹 Patient Education
As a nurse, your role goes beyond assessments and interventions. Teaching patients is key:
✅ Explain warning signs to report, such as heavy bleeding, contractions, or reduced fetal movement
✅ Reinforce the importance of prenatal visits
✅ Help families understand the plan of care and the need for possible hospitalization
Empowering patients with knowledge builds trust and improves outcomes.
👩⚕️ Cheat Sheet for NCLEX
✅ Placenta previa = painless, bright red bleeding, no vaginal exams
✅ Placental abruption = painful, dark red bleeding, rigid abdomen
✅ Prioritize maternal and fetal monitoring
✅ Prepare for cesarean if indicated
✅ Know the risk factors (previous cesarean, hypertension, trauma, substance use)
Add this quick guide to your nursing bundle for fast review before the NCLEX.
💡 Key Takeaways for RN Nurses
Placental complications are high-stress, high-stakes emergencies. As a registered nurse or RN nurse, you must act quickly, communicate clearly with the healthcare team, and provide ongoing emotional support for the family.