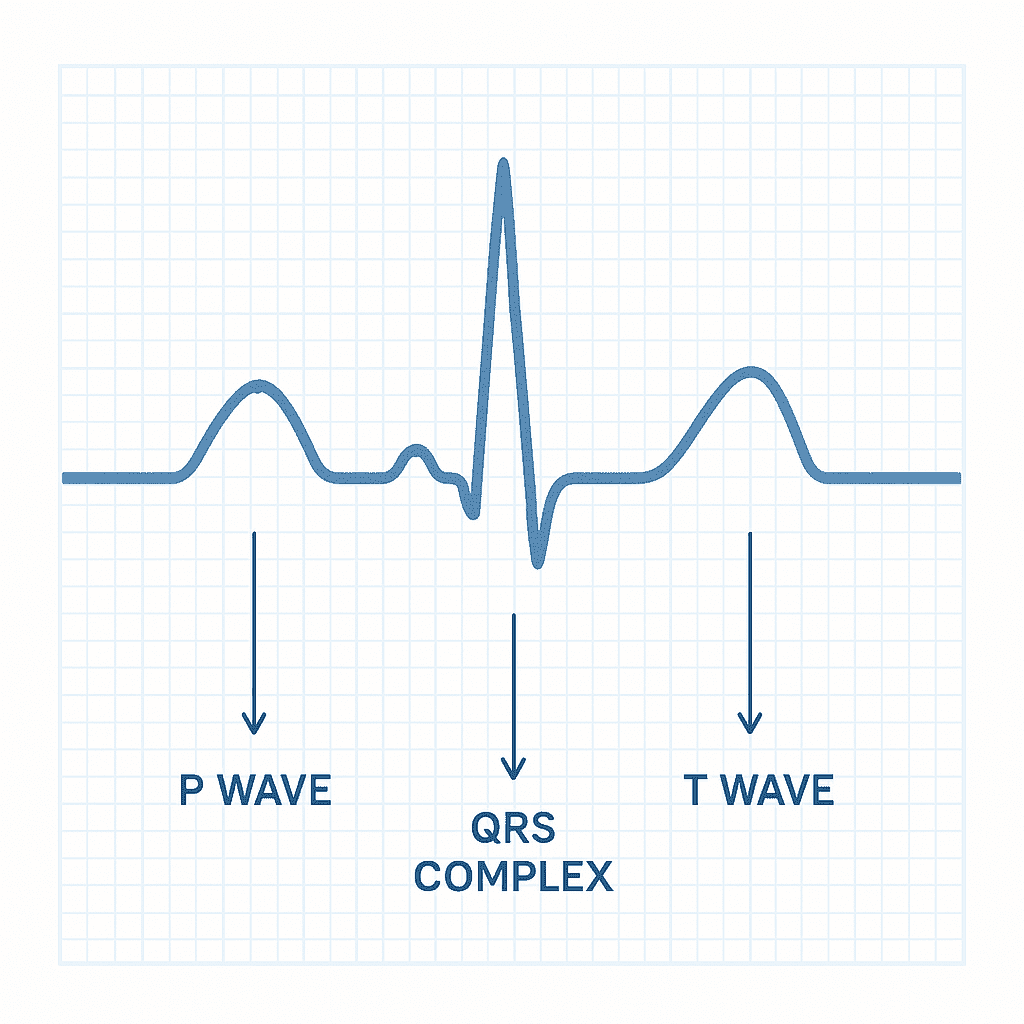
Electrocardiograms (ECGs or EKGs) are an essential part of nursing practice and NCLEX preparation. Understanding P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves is critical for every nurse, whether you are a student, a registered nurse (RN nurse), or reviewing concepts in a nursing bundle for quick study.
This article simplifies the ECG basics so that you can quickly identify normal vs abnormal patterns and apply them in practice.
🔹 The P Wave: Atrial Depolarization
- What it represents: The P wave reflects atrial depolarization (the electrical activity that causes the atria to contract).
- Normal characteristics:
- Small, rounded, upright in most leads
- Precedes every QRS complex
- Duration: ~0.06–0.12 seconds
👉 Nursing note: An absent P wave could mean atrial fibrillation or junctional rhythms. For the NCLEX, remember that irregular P waves often point to atrial issues.
🔹 The QRS Complex: Ventricular Depolarization
- What it represents: The QRS complex shows ventricular depolarization — the big contraction that pumps blood through the body.
- Normal characteristics:
- Sharp, tall, narrow spike
- Duration: <0.12 seconds
- Abnormal findings:
- Wide QRS: Possible bundle branch block or ventricular rhythm
- Tall R waves: Could suggest left ventricular hypertrophy
👉 Nursing note: During a Code Blue, wide QRS tachycardia is treated differently from narrow QRS tachycardia. As a nurse or registered nurse, distinguishing them is life-saving.
🔹 The T Wave: Ventricular Repolarization
- What it represents: The T wave reflects the ventricles resetting (repolarization) after contraction.
- Normal characteristics:
- Upright, smooth, rounded
- Asymmetrical (the second half is slower)
- Abnormal findings:
- Peaked T waves: May indicate hyperkalemia
- Inverted T waves: Can signal ischemia or infarction
👉 Nursing note: For NCLEX questions, always connect T wave changes with electrolyte imbalances and myocardial ischemia.
🔹 Putting It Together: A Quick Checklist for Nurses
When analyzing an EKG, RN nurses should ask:
- Is there a P wave before every QRS?
- Is the QRS complex narrow (<0.12 sec) or wide?
- Are the T waves upright and normal, or peaked/inverted?
This systematic approach helps nursing students and registered nurses catch dangerous rhythms quickly.
🔹 Why This Matters for NCLEX and Nursing Practice
- NCLEX tip: Expect questions that test your ability to match abnormal ECG changes to conditions like myocardial infarction, electrolyte disturbances, or arrhythmias.
- Nursing bundles: Many nursing bundles include ECG quick guides because this is such a high-yield topic for both exams and bedside care.
- Practical nursing: A nurse who can read ECG basics provides safer patient care and responds faster in emergencies.
✅ Final Thoughts
Mastering P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves is non-negotiable for every registered nurse and RN nurse preparing for the NCLEX. With practice and the right nursing bundle resources, you can quickly analyze an ECG strip and take action with confidence.