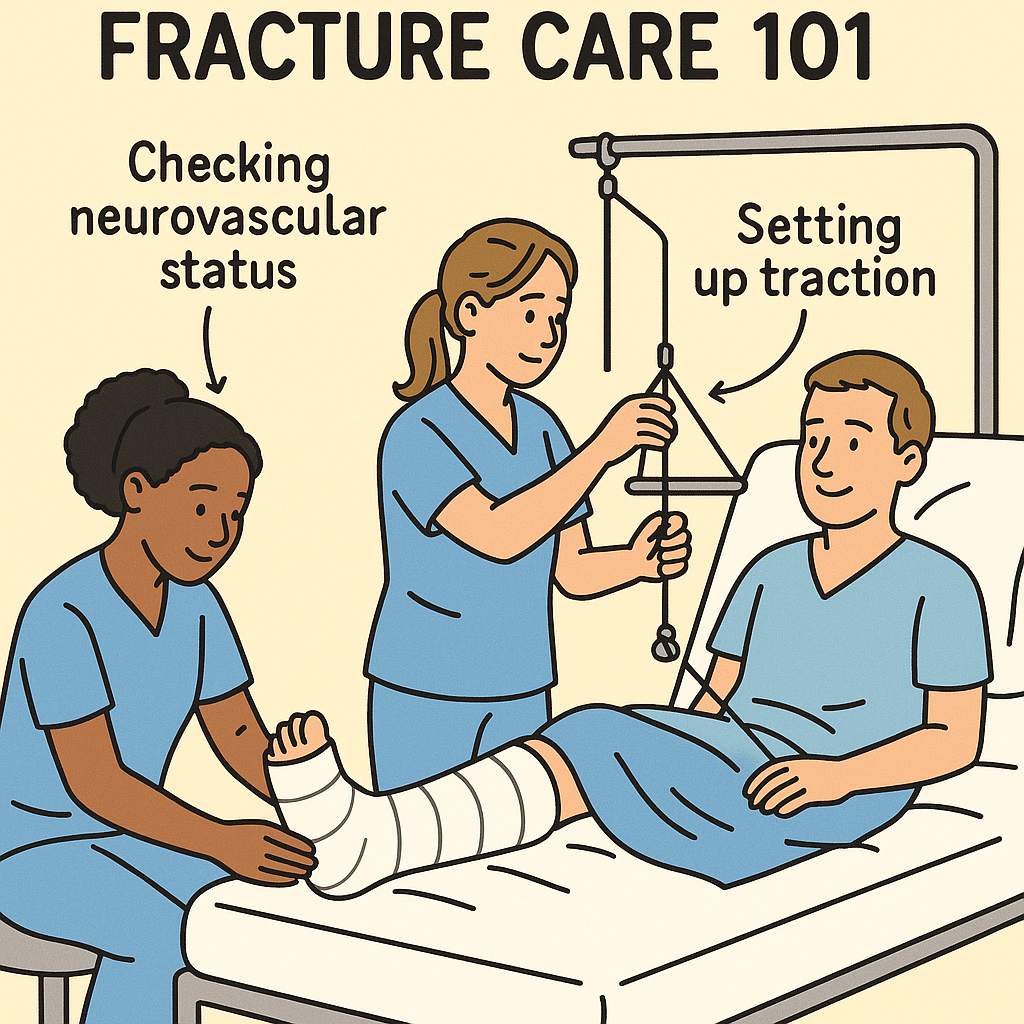
Fracture care is one of the most essential skills for every registered nurse (RN nurse), particularly those working in orthopedic and med-surg units. Proper management of casts, traction, and neurovascular checks not only ensures positive outcomes but also reduces complications. Moreover, this topic frequently appears on the NCLEX, making it a vital part of any nursing bundle.
🧠 Understanding Fractures
A fracture occurs when a bone breaks or loses its normal structure, often because of trauma, falls, or osteoporosis. When this happens, stabilizing the injury, relieving pain, and preventing further complications become the top nursing priorities. In addition, prompt recognition and intervention help prevent permanent damage and improve recovery.
🩹 Cast Care Basics
Casts are the most common method used to immobilize a fracture during healing. Therefore, nurses must understand the basics to ensure patient safety and comfort.
✅ Types of Casts
- Plaster: molds well and is cost-effective.
- Fiberglass: lighter, dries quickly, and is water-resistant.
✅ Key Nursing Actions
- Keep the cast dry and elevated to minimize swelling.
- Perform neurovascular checks every 1–2 hours during the initial phase.
- Observe for odor, drainage, or skin irritation.
- Remind patients not to insert any objects into the cast.
Furthermore, encourage movement of unaffected joints to prevent stiffness.
⚠️ Potential Complications
- Compartment syndrome (medical emergency)
- Skin breakdown and pressure sores
👉 NCLEX tip: Persistent pain that does not respond to medication may signal compartment syndrome — immediate intervention is required.
🪢 Traction Nursing Care
Traction helps realign fractured bones by applying a controlled pulling force. Depending on the case, it can be skin or skeletal traction.
- Skin traction (e.g., Buck’s traction): uses straps and weights attached externally.
- Skeletal traction: involves pins, wires, or screws inserted into the bone.
🩺 Nursing Responsibilities
- Maintain proper weight alignment and never remove weights without a provider’s order.
- Check ropes, pulleys, and alignment every shift for accuracy.
- Inspect the skin under straps or around pin sites.
- Perform frequent neurovascular checks to detect early complications.
- Use foot supports to prevent foot drop.
👉 NCLEX pearl: Traction weights must always hang freely — never resting on the floor or bed.
🔎 Neurovascular Checks
Consistent neurovascular assessment is vital for both casted and traction patients. To remember the essentials, think of the 6 Ps:
- Pain
- Pallor
- Pulses
- Paresthesia (tingling or numbness)
- Paralysis
- Poikilothermia (cool temperature)
Additionally, always compare both limbs, document findings thoroughly, and report any sudden changes without delay. Early intervention can prevent limb loss and other severe outcomes.
🧩 Nursing Bundle Cheat Sheet
Include the following in your nursing bundle for quick NCLEX and med-surg review:
- Cast care steps and assessment points
- Traction safety checklist
- 6 Ps neurovascular guide
- Early signs of compartment syndrome
This summary, when reviewed regularly, strengthens confidence in orthopedic care.
👩⚕️ Patient Education
Teaching patients and families is as important as direct nursing care. During discharge, make sure to educate them about:
- Signs of infection (fever, foul odor, or swelling)
- When to seek urgent care (increased pain, numbness, color change)
- Safe use of mobility aids (crutches, walkers)
- Cast and traction precautions
- The importance of follow-up X-rays
By empowering patients through education, nurses can significantly reduce complications and promote safe recovery.
⚠️ Watch for Complications
Throughout fracture management, nurses should remain alert for:
- Fat embolism syndrome (shortness of breath, confusion, petechiae)
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Pressure ulcers from immobility
- Muscle atrophy due to disuse
Recognizing these signs early allows prompt action and improves long-term outcomes.
📝 Quick Takeaways
- Casts: Protect skin, monitor circulation, and avoid inserting objects.
- Traction: Maintain alignment and ensure weights hang freely.
- Neurovascular Checks: Assess all 6 Ps every shift.
- Pain Management: Report unrelieved pain immediately.
Ultimately, consistent assessment, proper technique, and strong patient education form the foundation of effective fracture care. By mastering these skills, every RN nurse can ensure safer orthopedic recovery and NCLEX success.