Ventricular escape rhythms are critical cardiac rhythms that every nurse must recognize quickly. These rhythms often appear when higher pacemakers fail, and delayed identification can place a patient at serious risk. For nursing students, registered nurses, and RN nurses preparing for the NCLEX, understanding ventricular escape rhythms is essential for safe practice and exam success.
This guide explains ventricular escape rhythms in a simple, clinical way while highlighting key nursing responsibilities and NCLEX tips.
What Is a Ventricular Escape Rhythm?
A ventricular escape rhythm occurs when the ventricles take over as the heart’s pacemaker because the sinoatrial (SA) node and atrioventricular (AV) node fail to fire properly. As a result, the ventricles generate their own electrical impulse to maintain cardiac output.
Although this mechanism is protective, the rhythm is slow and inefficient, requiring close monitoring by the nurse.
Why Ventricular Escape Rhythms Matter in Nursing
From a nursing perspective, ventricular escape rhythms signal serious conduction system failure. Therefore, early recognition helps the registered nurse:
- Prevent cardiac arrest
- Initiate emergency protocols
- Prepare for pacing or advanced interventions
- Answer NCLEX cardiac rhythm questions accurately
In many cases, ventricular escape rhythms appear in unstable patients, making rapid nursing assessment crucial.
Causes of Ventricular Escape Rhythms
Several conditions can trigger this rhythm. Common causes include:
- Complete (third-degree) heart block
- Severe bradycardia
- SA node failure
- AV node dysfunction
- Drug toxicity (beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin)
- Myocardial infarction
- Severe hypoxia
Because medications play a role, nursing pharmacology knowledge—often reinforced through a nursing bundle—is vital.
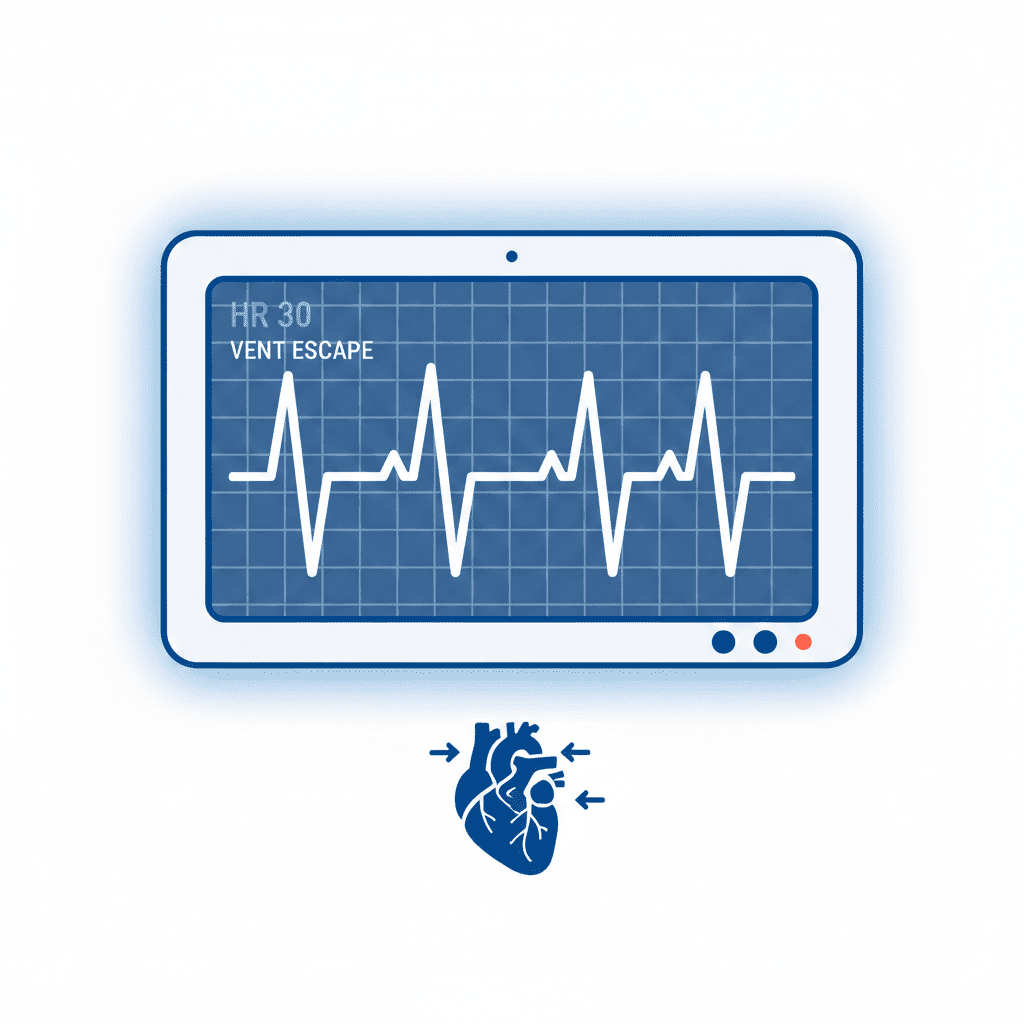
EKG Characteristics Nurses Must Recognize
Identifying ventricular escape rhythms on an EKG is a key RN nurse skill. Look for the following features:
- Rate: Very slow (usually 20–40 beats per minute)
- Rhythm: Regular
- P waves: Absent or unrelated to QRS
- QRS complex: Wide and bizarre (> 0.12 seconds)
- PR interval: Not measurable
On the NCLEX, these features help distinguish ventricular escape rhythms from junctional rhythms and idioventricular rhythms.
How Ventricular Escape Rhythms Differ from Other Rhythms
Unlike normal sinus rhythm or junctional escape rhythms, ventricular escape rhythms:
- Originate in the ventricles
- Produce wide QRS complexes
- Generate the slowest heart rates
- Indicate more severe conduction failure
Therefore, nurses must treat this rhythm as potentially life-threatening, not benign.
Nursing Assessment Priorities
Once a ventricular escape rhythm is identified, the nurse must immediately assess the patient, not just the monitor. Nursing priorities include:
- Checking blood pressure
- Assessing level of consciousness
- Monitoring oxygen saturation
- Evaluating chest pain or shortness of breath
- Identifying signs of poor perfusion
Importantly, the registered nurse should always correlate EKG findings with patient symptoms.
Nursing Interventions and Management
Management depends on patient stability. However, common nursing interventions include:
- Administering oxygen as ordered
- Preparing for transcutaneous or transvenous pacing
- Holding medications that suppress heart rate
- Notifying the provider immediately
- Ensuring IV access
- Continuous cardiac monitoring
In unstable patients, emergency pacing may be required. Thus, nursing readiness is critical.
NCLEX Tips for Ventricular Escape Rhythms
To succeed on the NCLEX, remember these key points:
- Ventricular escape rhythms are slow, wide, and dangerous
- The ventricles act as a backup pacemaker
- Wide QRS + absent P waves = ventricular origin
- Assess the patient first, then treat the rhythm
- Pacing is often the definitive treatment
Many nursing bundles include simplified EKG charts that make this rhythm easier to remember.
Patient Education Considerations
When the patient is stable, nurses may need to provide education. Teaching points include:
- Explaining the need for monitoring
- Discussing possible pacemaker placement
- Reviewing medication changes
- Encouraging follow-up cardiac care
Clear communication helps reduce anxiety and improves outcomes.
The Nurse’s Role in Cardiac Safety
Ultimately, identifying ventricular escape rhythms highlights the critical role of the nurse in cardiac care. Through rapid assessment, accurate EKG interpretation, and timely intervention, the RN nurse helps prevent life-threatening complications.
For nursing students and practicing registered nurses, mastering this rhythm strengthens both clinical confidence and NCLEX readiness.
Final Takeaway
Ventricular escape rhythms are a warning sign of serious conduction failure. Nurses who recognize the EKG patterns, assess patients promptly, and act decisively play a vital role in patient survival. Whether you are studying for the NCLEX or working at the bedside, this rhythm is one you must never miss.