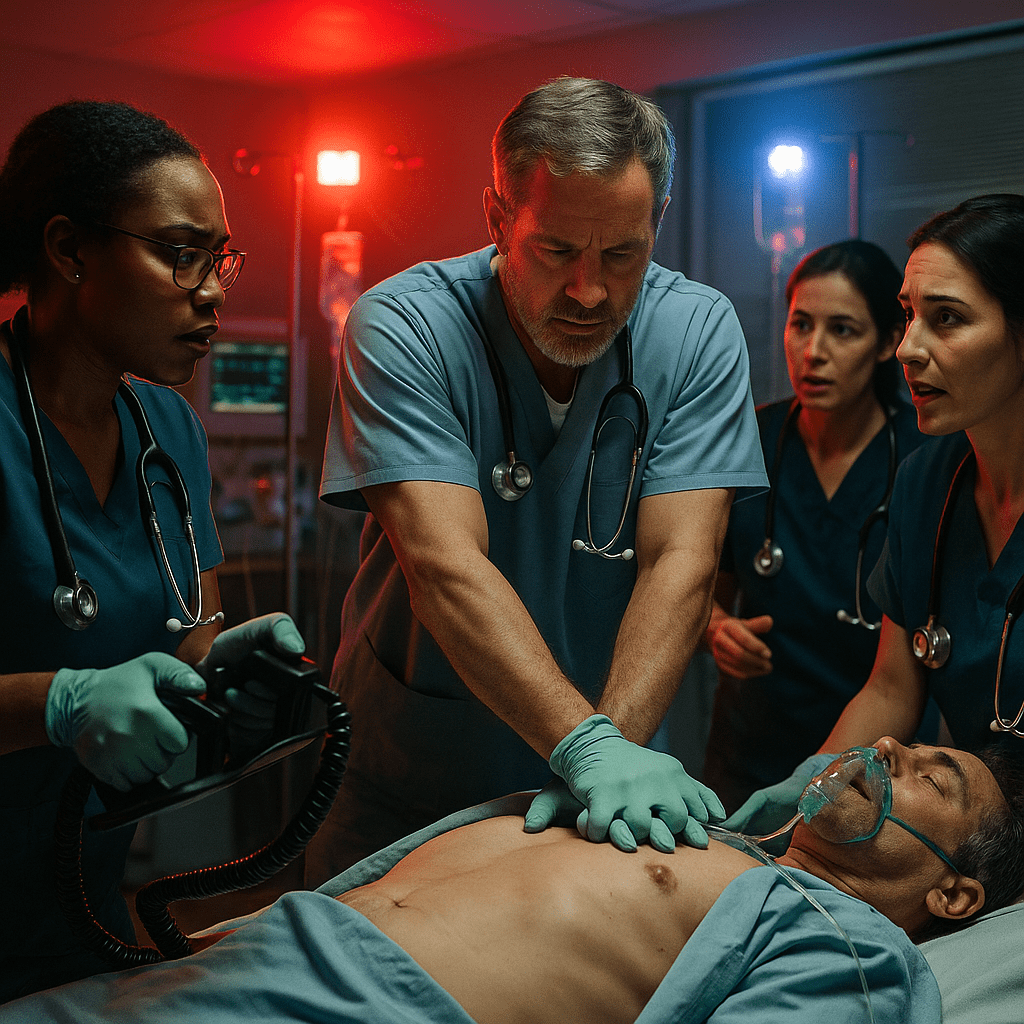When a Code Blue is called, every second counts. For every registered nurse (RN) and nursing student preparing for the NCLEX, understanding how to prioritize care during a cardiac or respiratory arrest is critical. The ability to act quickly, follow protocol, and maintain composure can mean the difference between life and death.
🚨 What Is a Code Blue?
A Code Blue refers to a medical emergency where a patient experiences cardiac arrest or respiratory failure, requiring immediate resuscitation. During this time, the nursing team, physicians, and other healthcare providers must work together efficiently to restore circulation and oxygenation.
For an RN nurse, being prepared for a Code Blue means understanding the Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) algorithms, which are both key areas on the NCLEX exam.
🧭 Nursing Priorities During a Code Blue
1. Assess Responsiveness and Call for Help
If you find an unresponsive patient, immediately call for help and activate the Code Blue team. The nurse who discovers the patient should also check for breathing and pulse while waiting for assistance.
🩹 Tip for NCLEX: Always assess first, then act. Early recognition saves time and improves survival rates.
2. Start Chest Compressions
If no pulse is detected, begin high-quality CPR:
- Rate: 100–120 compressions per minute
- Depth: At least 2 inches for adults
- Allow full chest recoil
- Minimize interruptions
As a registered nurse, your focus should remain on effective compressions until the crash cart and defibrillator arrive.
3. Defibrillation and Airway Management
When the defibrillator is ready, attach the pads and check the rhythm.
- If shockable (VF/pulseless VT) → Deliver a shock and resume CPR immediately.
- If non-shockable (asystole/PEA) → Continue CPR and administer medications per protocol.
A second nurse or respiratory therapist will manage the airway, providing bag-valve-mask ventilation or preparing for intubation.
4. Administer Emergency Medications
The RN nurse or code nurse administers medications such as:
- Epinephrine every 3–5 minutes
- Amiodarone for refractory VF/VT
- Atropine for bradycardia
Accurate timing, clear communication, and documentation are essential nursing responsibilities during this phase.
5. Maintain Clear Communication
Effective teamwork is the cornerstone of successful Code Blue management. Nurses should:
- Use closed-loop communication (repeat back orders to confirm understanding)
- Assign clear roles (compressor, recorder, airway manager, medication nurse)
- Document times of interventions, shocks, and medications
These communication strategies are often included in nursing bundles for emergency preparedness.
6. Post-Resuscitation Care
Once the patient regains circulation (ROSC — Return of Spontaneous Circulation), the focus shifts to:
- Stabilizing vital signs
- Initiating targeted temperature management (TTM)
- Monitoring cardiac rhythm and oxygenation
- Providing emotional support for the team and family
Post-Code Blue debriefs help registered nurses improve team coordination and learn from each event — a vital part of continuous professional growth in nursing.
🧠 NCLEX Tips for Nurses
If you’re preparing for the NCLEX, remember these key points about Code Blue scenarios:
- Prioritize airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs).
- Know the correct sequence of CPR and medication administration.
- Identify shockable vs. non-shockable rhythms.
- Maintain infection control and proper documentation.
Studying with an NCLEX nursing bundle or critical care nursing bundle can strengthen your knowledge of emergency algorithms, pharmacology, and team dynamics.
❤️ Nursing Takeaway
During a Code Blue, every registered nurse must stay calm, communicate clearly, and act efficiently. Prioritizing care through early recognition, effective CPR, and teamwork ensures the best possible outcomes. Whether in a real-life scenario or on the NCLEX exam, preparation and practice are the nurse’s most powerful tools.
💬 FAQ: Code Blue Nursing Priorities
The first action a nurse should take is to assess patient responsiveness and call for help by activating the Code Blue team. If the patient has no pulse, begin high-quality CPR immediately while waiting for the emergency team.
Each registered nurse (RN) on the team has a specific role:
Compressor: Performs chest compressions.
Airway nurse: Manages ventilation and assists with intubation.
Medication nurse: Administers emergency drugs.
Recorder: Documents all events, times, and interventions.