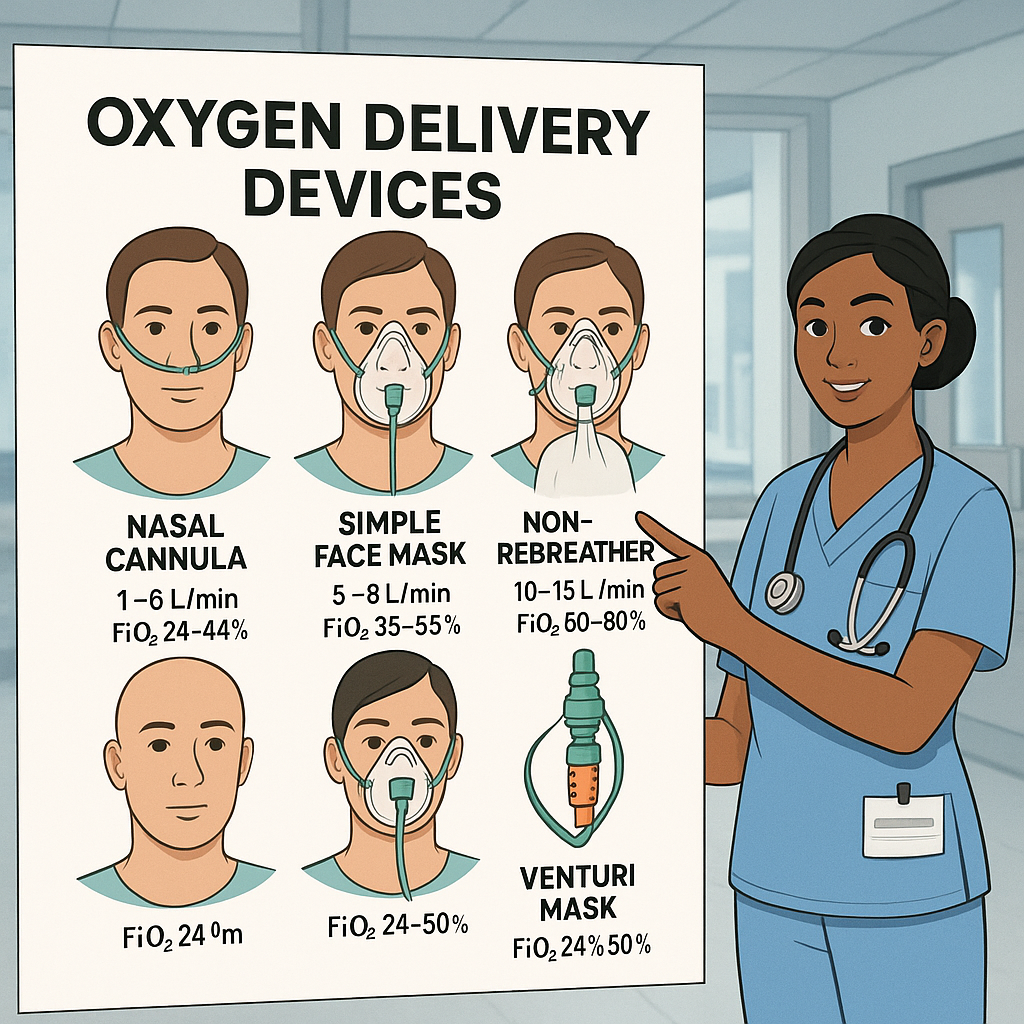
When it comes to oxygen therapy, nurses play a vital role in choosing the correct device, monitoring patient response, and ensuring safety. For the NCLEX exam, understanding the differences between oxygen delivery devices is essential, as questions often test a registered nurse’s knowledge of flow rates, FiO₂, and patient-specific considerations. This guide simplifies the oxygen delivery devices chart for every nurse, nursing student, or RN preparing for exams or clinical practice.
🌬️ 1. Nasal Cannula (NC)
- Flow rate: 1–6 L/min
- FiO₂ delivered: 24–44%
- Best for: Patients needing low-flow oxygen or supplemental support (COPD, stable patients).
- Nursing considerations:
- Watch for skin breakdown around ears/nares.
- Humidify if >4 L/min.
- Educate patients not to smoke or use open flames.
💡 NCLEX tip: Nasal cannulas are often the first choice for stable patients needing mild O₂ support.
😷 2. Simple Face Mask
- Flow rate: 6–10 L/min
- FiO₂ delivered: 40–60%
- Best for: Short-term use when more O₂ is needed than NC provides.
- Nursing considerations:
- Ensure a snug fit to prevent CO₂ rebreathing.
- Remove for meals when possible.
- Monitor for claustrophobia or discomfort.
💡 NCLEX tip: Never use <6 L/min with a simple mask—it risks CO₂ retention.
🛑 3. Non-Rebreather Mask (NRB)
- Flow rate: 10–15 L/min
- FiO₂ delivered: 60–100% (highest concentration without intubation).
- Best for: Emergencies like trauma, shock, or severe hypoxia.
- Nursing considerations:
- Ensure reservoir bag is ⅔ inflated before applying.
- One-way valves prevent exhaled air from mixing.
- Monitor closely for improvement or need for intubation.
💡 NCLEX tip: NRB is for acute respiratory distress and is a red flag device signaling severe O₂ needs.
🎯 4. Venturi Mask
- Flow rate: 4–12 L/min (depending on adapter).
- FiO₂ delivered: 24–50% (precise delivery).
- Best for: COPD patients requiring accurate O₂ concentration.
- Nursing considerations:
- Provides most accurate O₂ delivery without intubation.
- Use for patients with chronic CO₂ retention.
- Educate patients not to change adapters.
💡 NCLEX tip: Venturi = precise FiO₂ → COPD management.
📊 Quick Oxygen Delivery Devices Chart
| Device | Flow (L/min) | FiO₂ Delivered | Key Use Case | Nursing Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal Cannula | 1–6 | 24–44% | Stable, mild hypoxia | Skin care, humidify >4 L/min |
| Simple Mask | 6–10 | 40–60% | Short-term, moderate O₂ | Fit snug, no <6 L/min |
| Non-Rebreather | 10–15 | 60–100% | Emergencies, severe O₂ need | Reservoir inflated, monitor |
| Venturi Mask | 4–12 | 24–50% (precise) | COPD, controlled O₂ | Accurate FiO₂, no changes |
🩺 Nursing Takeaway
As a registered nurse, knowing when and how to use oxygen delivery devices is a life-saving skill. For NCLEX prep, remember:
- NC for stable patients.
- Simple mask for short-term moderate needs.
- NRB for emergencies (severe hypoxia).
- Venturi for COPD requiring precise O₂.
Every nurse and RN nurse should master this chart and include it in their nursing bundle of critical care knowledge.
🩺 FAQ: Oxygen Delivery Devices for Nurses
The four main oxygen delivery devices are the nasal cannula (NC), simple face mask, non-rebreather mask (NRB), and Venturi mask. Each delivers a different oxygen concentration and is used based on the patient’s oxygen needs and clinical condition.
A nasal cannula delivers 1–6 L/min, providing approximately 24%–44% FiO₂. It’s ideal for patients needing low-flow oxygen therapy and those who can breathe on their own.
A simple mask is used for patients who need moderate oxygen concentrations (about 6–10 L/min, 35%–60% FiO₂). Always ensure a minimum flow of 6 L/min to prevent CO₂ rebreathing.
Nurses choose based on:
SpO₂ levels and symptoms
Type of respiratory distress
Need for precise FiO₂ control
Patient’s ability to tolerate the device
Always assess breathing effort, comfort, and skin integrity.
Non-rebreather: Delivers high FiO₂ (up to 100%), used for emergencies.
Venturi: Delivers exact, fixed FiO₂, ideal for COPD or long-term oxygen therapy.