Respiratory conditions are critical for every nurse to understand, especially for the NCLEX and everyday practice as a registered nurse (RN nurse). COPD and asthma can sometimes look similar, but their causes, treatments, and long-term effects are very different. This guide will give you a straightforward nursing comparison to add to your nursing bundle of must-know information.
🫁 What Is COPD?
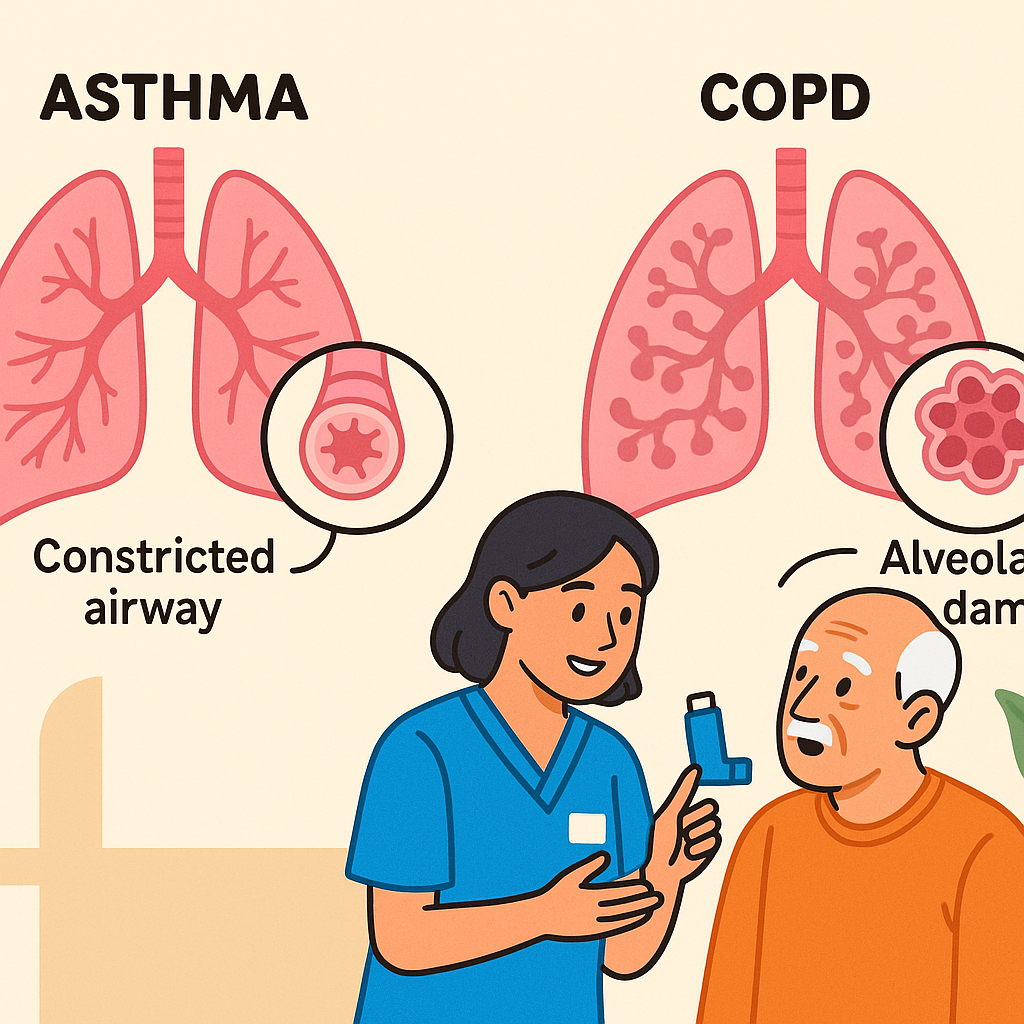
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive, irreversible lung disease that damages the airways and alveoli over time. The two main types are:
✅ Chronic bronchitis (mucus and inflammation)
✅ Emphysema (alveolar wall destruction)
Pathophysiology made simple:
- Long-term exposure to irritants (usually cigarette smoke)
- Airways become inflamed and narrowed
- Alveoli lose elasticity, trapping air
- Leads to chronic shortness of breath, wheezing, and cough
🫁 What Is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic, reversible airway disorder triggered by inflammation and bronchoconstriction.
Pathophysiology made simple:
- Exposure to a trigger (allergen, cold air, exercise)
- Airways narrow and swell
- Bronchial smooth muscle contracts
- Mucus production increases
- Symptoms include wheezing, chest tightness, cough
🎯 NCLEX Nursing Bundle Quick Facts
- COPD = not reversible, progressive
- Asthma = reversible, episodic
- COPD: constant symptoms
- Asthma: symptoms come and go
- Both: treat with bronchodilators, steroids
💡 NCLEX tip: If you see pink puffer or blue bloater in a question, think of COPD. Asthma often links to childhood or allergies.
Add this to your nursing bundle so you can quickly recognize the differences.
🩺 Key Nursing Assessments
COPD
✅ Barrel chest (from air trapping)
✅ Chronic cough with sputum
✅ Clubbing of fingers
✅ Accessory muscle use
✅ Diminished breath sounds
Asthma
✅ Expiratory wheezing
✅ Prolonged expiration
✅ Sudden chest tightness
✅ Anxiety during attack
✅ Symptoms relieved with bronchodilators
🩺 Nursing Interventions
For both COPD and asthma:
✅ Assess airway and breathing frequently
✅ Position patient upright to ease breathing
✅ Administer oxygen as prescribed (be cautious in COPD patients to avoid too much O2)
✅ Give bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol)
✅ Administer corticosteroids for inflammation
✅ Teach proper inhaler technique
✅ Encourage smoking cessation (for COPD)
✅ Monitor peak flow if asthmatic
Patient Education
- For asthma: avoid triggers and learn action plans
- For COPD: conserve energy, monitor for infections, get flu/pneumonia vaccines
🩺 Registered Nurse Priorities
As a registered nurse, you must watch for:
- Severe respiratory distress
- Inability to speak in full sentences
- Drop in oxygen saturation
- Confusion or drowsiness (signs of CO2 retention)
- Signs of status asthmaticus (asthma attack not responding to treatment)
📚 Add This to Your Nursing Bundle
Include:
✅ COPD vs. asthma comparison chart
✅ Inhaler medication cheat sheet
✅ NCLEX-style practice questions
✅ Patient teaching handouts
These tools will help every RN nurse feel confident about these high-yield respiratory conditions.
🧠 Quick Recap
| Condition | Key Features | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| COPD | Irreversible, chronic, progressive | Bronchodilators, oxygen, steroids |
| Asthma | Reversible, episodic | Bronchodilators, trigger avoidance, steroids |